Is your moisturizer a fire hazard? Researchers say fabrics with dried emollients catch fire in less than 20 seconds
06/05/2019 / By Michelle Simmons
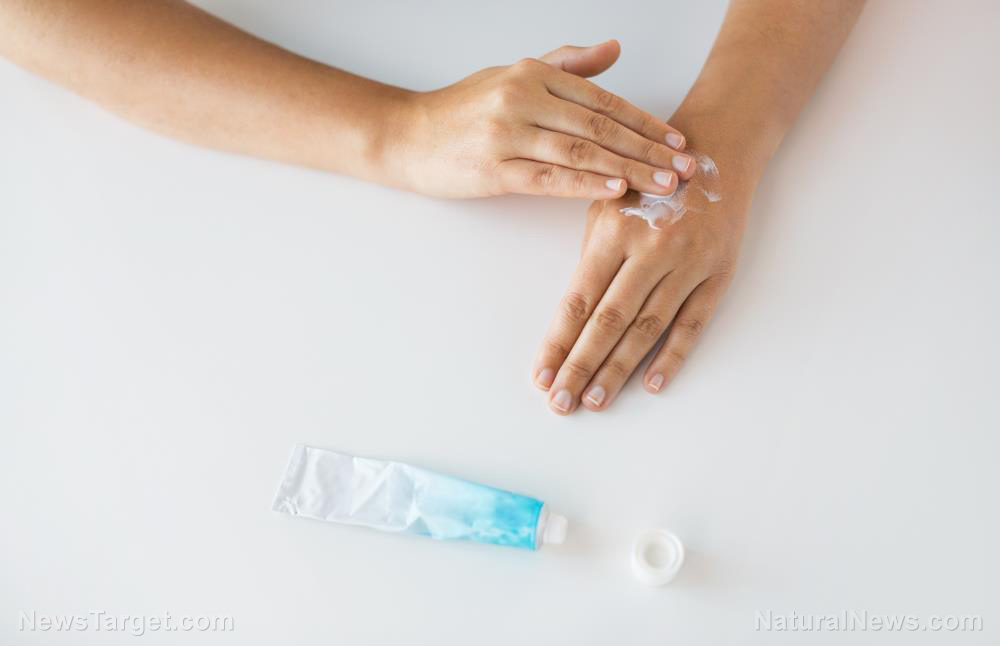

Beware of the moisturizers you’re using because they could cause a fire. A study published in the Fire Safety Journal showed that commonly used emollients or non-cosmetic moisturizers are a fire hazard once they have dried on fabric, such as clothing and bedding.
For the study, forensic scientists at Anglia Ruskin University in the U.K. examined various moisturizers, such as those typically used for treating skin problems, such as eczema and psoriasis. Initially, they focused on creams, lotions, and ointments with paraffin bases. However, their latest laboratory research revealed that the presence of paraffin-free emollient increases the flammability of fabrics.
In conducting the study, they measured the time it takes for fabrics – such as cotton of different thread counts and polyester-cotton blend – to catch fire once contaminated with a moisturizer and in the proximity of a naked flame. The results showed that non-contaminated fabrics took an average of one minute and five seconds or 65 seconds to burn; those with emollient residue ignited in less than 20 seconds.
The researchers emphasized that people should be aware that when emollients come into contact with fabrics, clothes, bedding, or bandages, they can easily catch fire with smoking materials like matches and lighters, naked flames, or other sources of heat. In addition, they called out people who prescribe, dispense, or apply these products that using a lower or paraffin-free emollient as an alternative will not lower the risk of fire. Even washing fabrics contaminated with these products may not completely remove the fire risk, because the chemicals can become dried in — but it may reduce the risk.
“We are now carrying out further research to try and identify any common ingredients as well as the best ways of removing the residue from clothing and bedding, for example the ideal washing temperature,” said Sarah Hall, senior lecturer in forensic science and one of the authors of the study. (Related: Beat Big Pharma drug prices and chemical additives – Make your own safe, high quality, natural topical ointments at home.)
Alternative treatments for skin conditions
Eczema and psoriasis are different conditions, but they have the same symptoms of painfully dry, tight, and itchy skin. While many eczema and psoriasis treatments need topical care, most of the time, these skin conditions are needed to be healed from the inside. Here are some foods that can help treat eczema and psoriasis.
- Flaxseeds: Flaxseeds are loaded with omega-3 fatty acids, and these fatty acids help suppress a chemical in the body called arachidonic acid which causes inflammation. To add flaxseed to your diet, grind up a few tablespoons of it and then add to your granola, oatmeal, salads, or smoothies. You can also use flaxseed oil as a dressing for salads and vegetables.
- Turmeric: Turmeric is known to reduce inflammation in many skin conditions, including eczema and psoriasis. Turmeric contains an antioxidant called curcumin, which is reported to protect skin by neutralizing free radicals and speeding up the healing time of wounds. For best results, take about a teaspoon of turmeric every day. You can add it to rice, pasta, vegetables, and other cooked meals because of its subtle, citrusy flavor.
- Fatty fish: Like flaxseeds, fatty fish contains omega-3 fatty acids that help with eczema and psoriasis. To reap its benefits, aim to consume at least three 3 to 4-ounce servings fatty fish every week.
Know what’s inside the products you use. Learn more at Chemicals.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: cosmetics, creams, eczema, emollients, fabrics, fire hazard, flammable, lotion, lotions, moisturizers, personal care, products, psoriasis, research, safety, skin care, skin conditions, toxic chemicals, toxic ingredients, warning
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 WEIRDSCIENCENEWS.COM
All content posted on this site is protected under Free Speech. WeirdScienceNews.com is not responsible for content written by contributing authors. The information on this site is provided for educational and entertainment purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional advice of any kind. WeirdScienceNews.com assumes no responsibility for the use or misuse of this material. All trademarks, registered trademarks and service marks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.